Wire ropes are indispensable tools in various industries, offering unparalleled strength and durability for lifting, pulling, and securing heavy loads. Understanding how wire ropes are classified is crucial for selecting the right type for specific applications. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the composition, structure, classification, and factors to consider when choosing wire ropes.
1. What is a Wire Rope?
A wire rope is made of multiple steel wires twisted together in a spiral. Since they’re made of steel, wire ropes are extremely strong, flexible, and wear-resistant.
2. Components of Wire Rope
Wire ropes consist of three primary components:
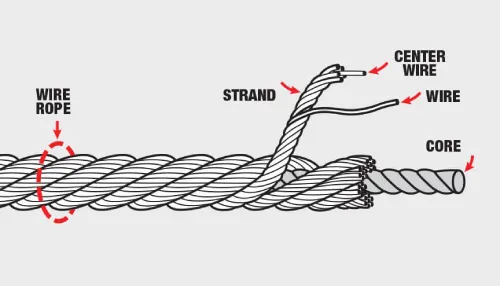
3. Structure of Wire Rope
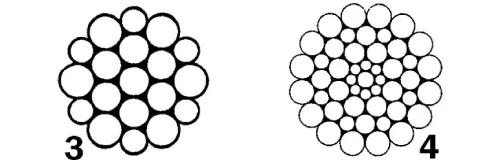
Wire ropes come in various structures, each designed to meet specific requirements. Common structures include:
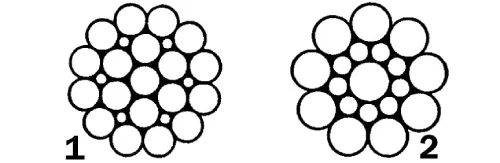
- Filler Wire Rope: This consists of a core surrounded by one or more layers of wires, providing flexibility and strength.
- Seale Wire Rope: Features a central core surrounded by strands twisted in the opposite direction, offering increased stability and resistance to crushing.
- Warrington Wire Rope: Utilizes a combination of large and small outer wires to distribute loads evenly, enhancing durability and flexibility.
- Swaged Wire Rope: Comprises compacted strands for enhanced strength and abrasion resistance.
4. Wire Rope Lay Direction
The “lay direction” of a wire rope depends on whether its wires twist left or right during production. The lay direction can be either right-hand (clockwise) or left-hand (counterclockwise), affecting the rope’s performance and longevity.
5. Representation of Different Structures
Different wire rope types are labeled with simple codes.. For example:
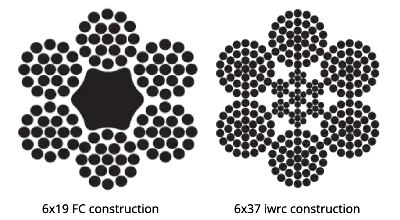
- A filler wire rope may be described as “6×19 FC” (6 strands, 19 wires per strand, fiber core).
- A seale wire rope might be described as “6×37 IWRC” (6 strands, 37 wires per strand, independent wire rope core).
6. Classification of Wire Rope
Wire ropes can be classified based on various criteria, including surface condition, material composition, and application. Examples of classification methods include:
- Surface Condition: Galvanized, ungalvanized, or coated wire ropes.
- Material Composition: Stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloy steel wire ropes.
- Application: Crane ropes, elevator ropes, or mining ropes.
7. Factors to Consider When Selecting Wire Rope
When choosing a wire rope, consider::
- Load Capacity: Ensure the wire rope can support the intended load safely.
- Durability: Consider the environment and conditions the wire rope will be exposed to.
- Flexibility: Select a wire rope with the appropriate flexibility for the application.
- Safety: Choose a wire rope that meets relevant safety standards and regulations.
In conclusion, understanding the composition, structure, classification, and selection factors of wire ropes is essential for ensuring safety and efficiency in various industrial applications. By considering these factors carefully, you can choose the right wire rope to meet your specific needs and requirements.
